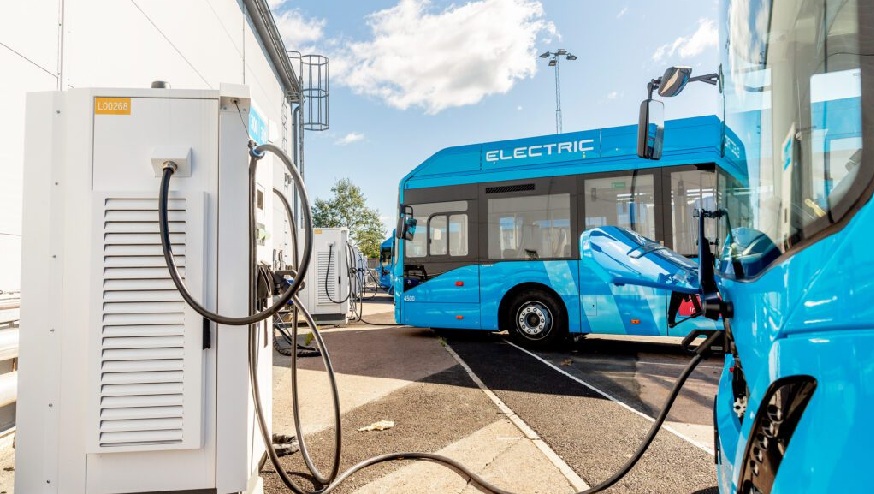
Decommissioned batteries from Nobina’s electric bus fleet will be repurposed in storage systems rather than subjected to early and costly recycling.
Following a successful pilot project, battery storage systems will be installed in the countries where the Nordic region’s largest public transport operator operates – Sweden, Finland, Norway, and Denmark- and managed by Nobina to support the grid.
Additionally, local grids will be stabilized, and excess electricity will be available for trading on the spot market.
Every day, the company covers a distance equivalent to circling the globe 23 times, transporting approximately one million passengers.
Nobina currently has more than 1,000 e-buses in its total fleet of 5,000 buses, with an estimated total battery capacity of around 500 MWh.
Petra Hammarin, Business development director at Nobina, says: “This sustainability initiative not only enhances our operational resilience and reduces energy costs but also minimizes Europe’s dependence on critical minerals and helps stabilize local power grids – a truly circular and sustainable approach,”
She continues: “Battery storage systems using decommissioned bus batteries could be a vital component for both competitiveness and sustainability,” adds Petra Hammarin.
Nam Truong, CEO & Co-Founder of STABL Energy, states: “We see great potential for Nobina to extend the lifespan of batteries through stationary storage applications when they are no longer suitable for vehicle use. This provides a resource-efficient alternative to premature and expensive recycling, which removes batteries from the cycle far too early.”
“The resource-efficient use of batteries is also of immense strategic importance for Europe from a geopolitical perspective, as it strengthens the circular economy and reduces dependency on raw materials,” Truong adds.
Nobina AB electric bus charging for efficient and emission-free mobility
Investment in fleet electrification is high.
By utilizing modular multilevel inverter technology, which enables the construction of battery storage systems using second-life batteries, investment costs for e-vehicles can be offset through the continued use of batteries, making operations more efficient.
This provides a cost-effective alternative to the current recycling process, which remains unattractive and expensive when all associated processes are considered.
Furthermore, since battery production already emits greenhouse gases, second-life applications ensure that batteries contribute to further CO2 emission reductions throughout their entire lifespan.
READ MORE
-
Checkmate: Tridens facilitates CPO migration after Landis exits EV charging business
The migration to the Tridens EV Charge platform ensures operational continuity, scalability, and compliance with international technical standards for CPOs. While the company currently has over 100 clients worldwide, including prominent players such as Siemens, BYD, ABB, and Shell, Tridens is now seeking new target clients.
-
Daimler Truck plans to build Europe’s largest semi-public charging network
Semi-public charging provides eTruck owners a larger scale of cost-efficient charging opportunities and enables site operators to open their depot charging infrastructure up to third parties
-
EnBW backtracks on its goals: Will install fewer chargers than planned
At the end of 2023, EnBW announced it would double its annual investment in the development of fast charging infrastructure in Germany to €200 million euros and aimed to operate 30,000 fast charging points in the country by 2030. However, this will no longer be the case. How many chargers does it now plan to…